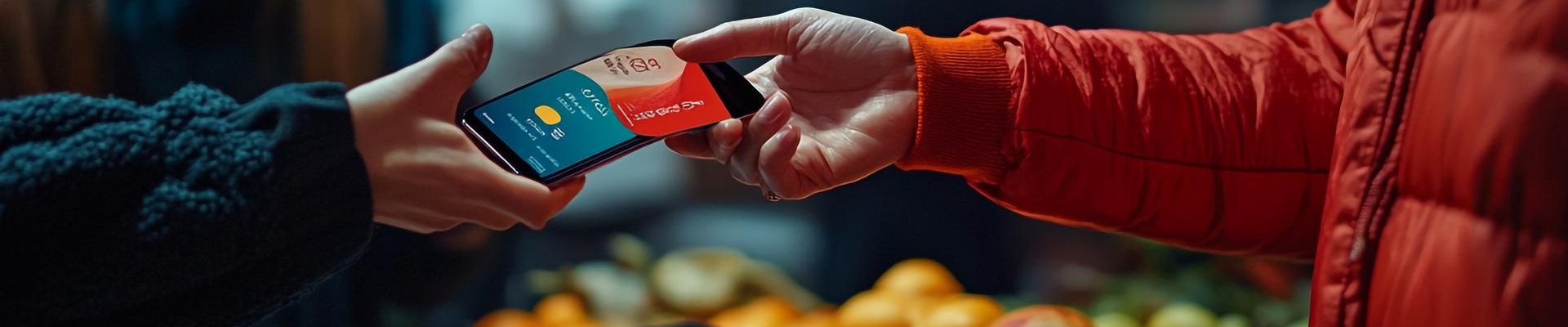
The Global March towards Cashless Economies
In recent years, the world has seen a significant shift toward cashless
transactions, with governments, businesses, and consumers adopting digital
payment solutions at unprecedented speed. While the vision of a fully cashless
economy once felt distant, technological innovation and policy support have
rapidly accelerated its global momentum.
Global Trends and Regional Leaders
Countries like Sweden and South Korea are at the forefront, with digital
transactions making up the vast majority of payments. China has normalized QR-code
based mobile payments through platforms like WeChat Pay and Alipay, even in
informal markets. India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has transformed
digital payments for millions, enabling even small vendors and rural users to
participate in the cashless ecosystem.
Drivers of Cashless Growth
The growth of mobile internet, smartphones, fintech innovations, and real-time
payment infrastructure has made going cashless more accessible than ever.
Governments are also playing a critical role — incentivizing digital payments,
introducing central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and reducing dependency on
physical currency.
Advantages and Challenges
Cashless systems offer several benefits: improved transparency, lower handling
costs, financial inclusion, and faster transactions. However, they also raise
concerns — such as cybersecurity threats, data privacy issues, and the risk of
excluding unbanked or digitally illiterate populations.
The Road Ahead
While full cash elimination may not be practical or even desirable in every
context, the shift toward digital-first payment systems is undeniable. The goal
ahead is to ensure that this transformation is secure, inclusive, and adaptable
to the diverse needs of citizens worldwide.
As cashless initiatives continue to evolve, the most successful models will be
those that strike the right balance between technology, trust, and accessibility
— creating a future where money moves smarter, faster, and safer.
















.png)




.png)









.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
















.png)



.png)














































































.png)